
RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 ifconfigĮth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:21:9b:62:d0:4a It is just simple 2-3 line configuration required to set up a USB adapter as monitor interface for wireshark.
#WIRESHARK HTTP DECODE HOW TO#
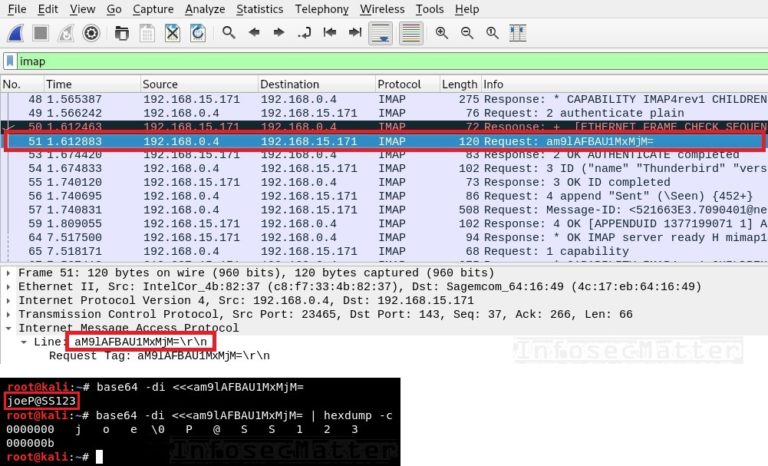
I have used BackTrack with USB adapter to take this packet capture ( Refer this youtube video for how to do it). Simply what you have to do is take a “wireless packet capture” on CH 36 as my AP operate in that channel. I am using 5GHz & therefore get 802.11a summary here (If you want sniff 2.4GHz, then you can issue command with 802.11b) (4402-3) > show ap config 802.11a summaryĪP Name SubBand RadioMAC Status Channel PwLvl SlotId Otherwise you can simply use application like InSSIDer to see which channel given SSID is operating. Since my AP is managed by WLC 4400, I can simply get that info from CLI. This is useful when you study (my case for CWSP studies) different security protocols used in wireless.Here is the basic topology for this post.īefore start capturing you should know which channel your AP is operating. You should see something like the following (we modified the example slightly to display only the secret keys).In this post we will see how to decrypt WPA2-PSK traffic using wireshark. Finally, load the application to the module. To log the data directly, go to Transfer->Log to File (text) from the top menu and select where you’d like to save the data.

This will prevent you from having to do a lot of reformatting to the keys like you would if you were to simply copy and paste.
#WIRESHARK HTTP DECODE SERIAL#
If you’re using MTTTY for your serial terminal, we recommend that you log the serial data directly to the file. The flags -no_ticket and -no_cache will prevent connections from using session resumption, which will make our lives a tad easier when trying to decrypt the packets from Wireshark.Īfter we’ve started the server, go ahead and start listening for the packets on Wireshark. The flag -accept just dictates what port the SSL server will accept connections on. For more info on that, see our article on self signed certificates. We generated ours using the certificate generation scripts provided with the NNDK tools. Note that you’ll need to have a certificate ( -cert) and key ( -key) handy. Openssl s_server -key Server.key -cert Server.crt -accept 4433 -no_ticket -no_cache For this we use this OpenSSL command from the command line:
The second is to actually start the SSL server that will receive the connection. Simply change the macro SSL_SERVER_NAME to the proper IP address, and rebuild the application. The first is to add the IP address of your SSL server to the example. You can find this example in \examples\SSL\sslclient.įor this example, you’ll need to do two things in addition to the system changes above. It very simple, and shows how the NetBurner device can connect to an SSL server.
#WIRESHARK HTTP DECODE CODE#
Example Code Changesįor the purpose of this article, we’ll be using our 3.x tools and will do our testing with the SSL client example. If you’re using our NNDK 2.x tools, you’ll need to rebuild the system libraries separately before building the application. If you’re using our latest tools, either with NBEclipse or via the command line, everything is taken care of when you rebuild the project itself, as all of the system libraries are included as a part of this process. Now, choose any SSL/TLS example, or if you’re already working on your application, rebuild the system libraries and the project. Without this secret key, neither side can decrypt any messages that are encrypted by the other side. In every secure SSL/TLS connection, information sent back and forth between the client and server is encrypted using a secret key (also called a premaster secret) that is generated by the client during the TLS handshake. We won’t dive too far into the TLS handshake in this article, but having a basic understanding of how it works will help explain what we need to do in Wireshark. Finally, we’ll show what it looks like in action. Then we’ll look at how to get that information from the NetBurner device. First, we discuss what information needs to be set in Wireshark and demonstrate how to do it. In this article, we’ll cover the steps you have to go through to get to this goldmine of debugging goodness.
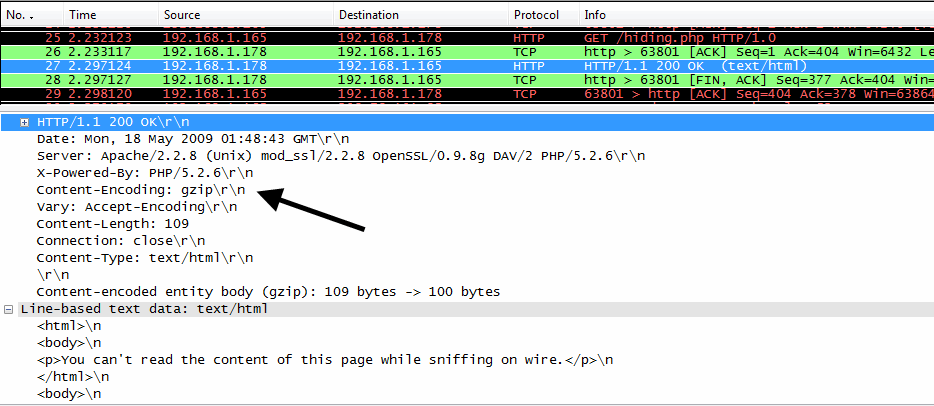
Given the proper information, Wireshark can decode this information for you and let you see exactly what’s being sent over the wire. Unfortunately, that doesn’t help you as you’re staring at the mix of unfamiliar garbage sitting in front of your face.įortunately, there is hope. Maybe you know what it’s supposed to say. Trying to debug issues over an encrypted connection with Wireshark is a lot like trying to edit an article in a language you don’t know. Most of this looks great, until you actually look at the data, and are greeted with, “Encrypted Application Data: ”.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
